What is glaucoma?
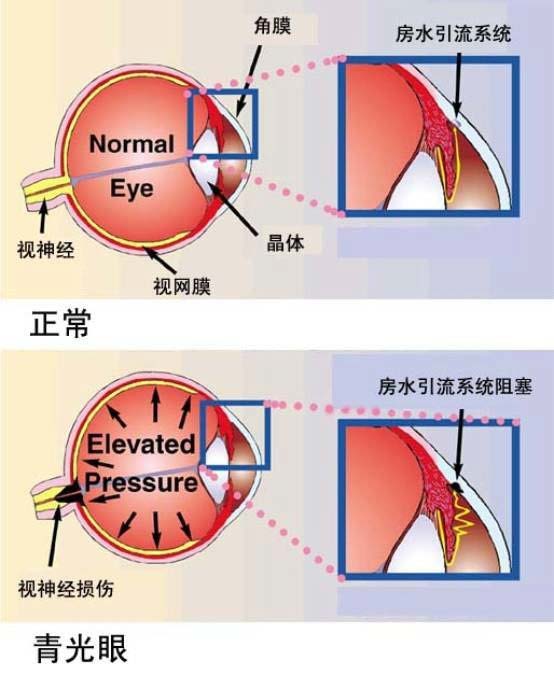
There is a transparent liquid called "aqueous humor" in the human eyeball. This watery fluid constantly flows inside the eye. If the corpus callosum secretes too much aqueous humor or the drainage system is blocked, intraocular pressure will rise and damage the optic nerve, eventually leading to blindness. This disease is called glaucoma.
The characteristic of glaucoma is that the optic nerve is compressed and atrophied, resulting in loss of peripheral vision. Most glaucoma is painless and difficult to detect in the early stages of the disease, so it is called the thief of vision. It is one of the main causes of blindness in adults worldwide.
Acute glaucoma
About one-third of patients have acute glaucoma, with symptoms of severe eye pain, headache, rapidly blurred vision, nausea and vomiting. Patients seek medical attention because of the pain caused by acute attacks.
If one eye develops glaucoma, there is a 95% chance that the other eye will develop glaucoma within five years. So be sure to receive preventive treatment.
Chronic glaucoma
Two-thirds of patients suffer from chronic glaucoma. In the early stages of the disease, their vision remains normal, their eyes are not red or painful, and their central vision may also be maintained. It is not until the late stages of the disease that they notice the abnormality when their peripheral vision is completely lost. The range of vision they see is like looking out of a tunnel. Over time, they become completely blind. Initial diagnosis can be made by measuring intraocular pressure and doing a visual field test.
The following are more likely to develop glaucoma
- Diabetes, high blood pressure, migraines
- People with a family history of glaucoma
- Elderly, eye trauma, severe myopia
- People who have taken steroids in the past or are currently taking them
Prevention of glaucoma
Vision loss caused by glaucoma cannot be reversed. Prevention is better than cure. If a close relative has glaucoma, you should have regular eye examinations. In fact, whether you develop glaucoma depends on the level of intraocular pressure that the optic nerve can withstand, and this number varies from person to person.
Normal intraocular pressure is generally between 12 and 21 mm Hg. Even if the intraocular pressure remains within this range, you may still develop glaucoma, which is called "normal-tension glaucoma". Therefore, it is very important to have an eye examination. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, further vision loss can be prevented or slowed.
Glaucoma Examination
Regular eye examinations are important for monitoring glaucoma and preventing serious and permanent vision loss. Ophthalmologists can diagnose glaucoma through different tests, including:
- Measuring intraocular pressure
- Optic nerve examination - dilating the pupil to examine the condition of the retina and optic nerve
- Visual field analysis - measuring peripheral vision, and narrowing of the visual field is a sign of glaucoma
- Gonioscopy - examining the drainage channels in the anterior chamber of the eye
- Optic disc tomography (OCT), Heidelberg retinal tomography (HRT3) - allowing doctors to diagnose, observe and treat glaucoma more effectively and accurately
Glaucoma Treatment
The most effective way to treat glaucoma now is to reduce intraocular pressure to an appropriate level. Eye drops, oral medications, lasers, and surgery are all ways to lower intraocular pressure and prevent further vision damage.
PI (Peripheral Iridotomy) Peripheral Iridotomy
SLT (Selectice laser Trabeculoplasty) Selective laser trabeculoplasty
MLT (micropulse laser trabeculoplasty) Micropulse laser trabeculoplasty
Eye drops and oral medication: It is the most commonly used method. Patients must use it on time to reduce intraocular pressure. Generally speaking, once the optic nerve is damaged, it cannot recover. The only thing that can be done is to control the intraocular pressure and stabilize the condition, rather than cure it. Patients need to use eye drops for a long time.
Common side effects of eye drops are mild redness and pain after application, which is nothing to worry about.
Oral medication can have a diuretic effect, and you may also feel numbness in your lips and fingertips.
Surgery: This is usually used when medication and laser surgery cannot control glaucoma.
Laser: Usually used when eye drops cannot control the condition, and can also be used together with drugs to reduce intraocular pressure.