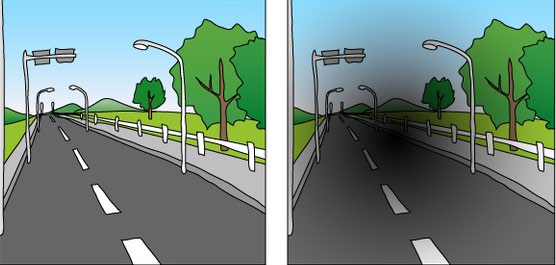
What is maculopathy?
The macula is the central area of the retina and is responsible for central vision. Its main function is to distinguish colors and observe fine objects, such as reading, writing, driving, or threading a needle.
If the macula degenerates, causing damage to central vision, it is called macular degeneration.
What are the symptoms of macular degeneration?
• Blurred central vision
• Darkening of colors or problems distinguishing colors
• Distortion of objects or distortion of straight lines
• Darkening or blackening of the center of the object
What types of macular degeneration are there?
1. Age-related macular degeneration: Most patients are over 50 years old and can be divided into dry and wet types. It has become the number one cause of blindness in Western countries.
2. Pathological myopic macular degeneration: patients with myopia of 600 degrees or more are more likely to suffer from it
3. Macular perforation, macular membrane
4. Macular edema
Causes of age-related macular degeneration
Studies have shown that it is related to the following factors: age, smoking, high blood pressure and family inheritance, as well as exposure to ultraviolet rays and lack of balanced nutrition
Prevention methods for age-related macular degeneration
• Quit smoking and reduce high-fat foods
• Taking antioxidants, vitamins A, C, E and minerals such as zinc can delay the decline of macular degeneration
• Wearing sunglasses that block ultraviolet light
• Go to an ophthalmologist for regular eye examinations and early treatment
What are the examination methods?
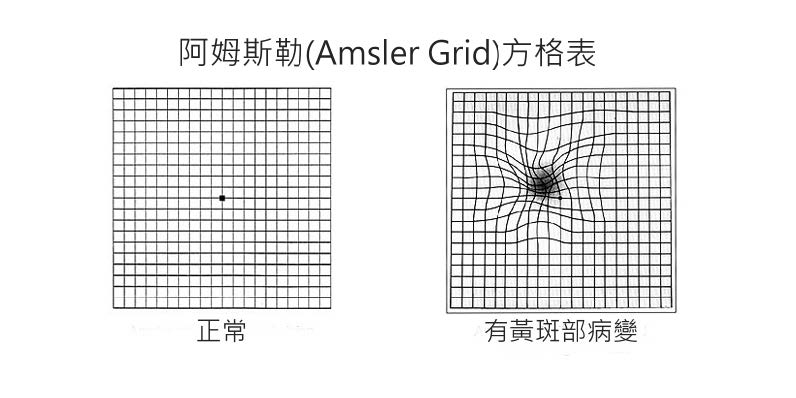
1. AMSLER GRID
A simple self-check method for age-related macular degeneration.
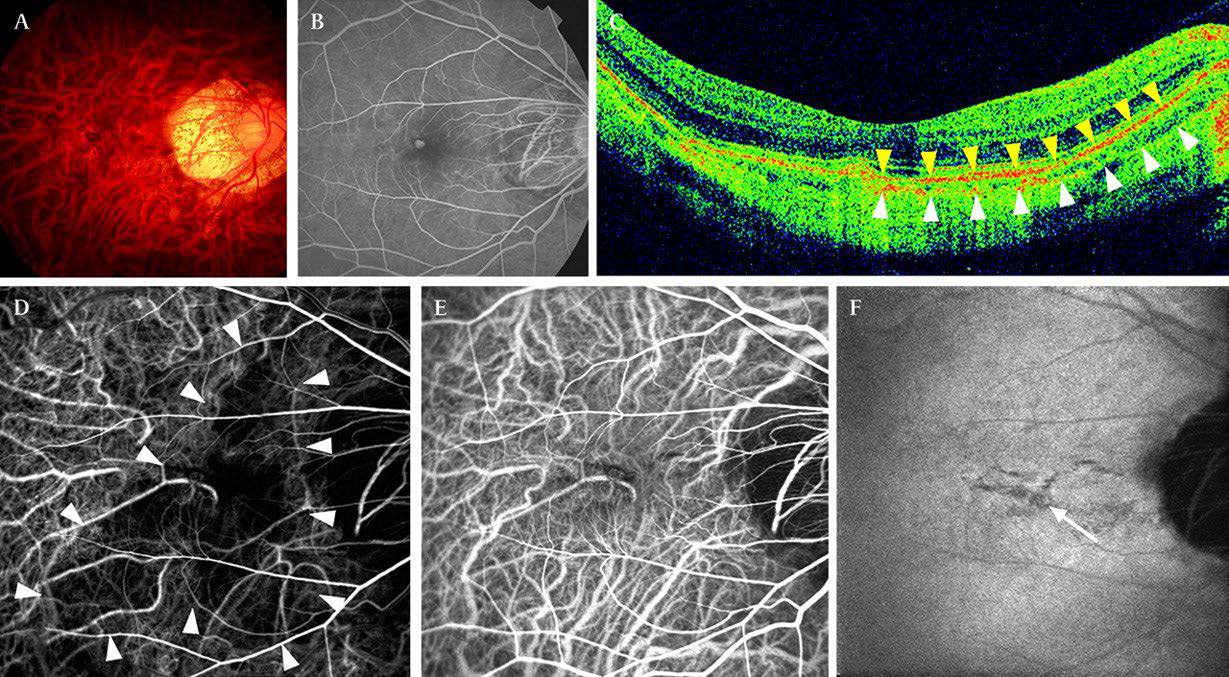
2. Flourescein Angiogram and Indocyanine Green Angiography
The ophthalmologist first injects a fluorescent contrast agent into the patient's vein to reveal the blood vessels in the retina through the image, thereby understanding the condition of the patient's new blood vessels in the retina and making a diagnosis.
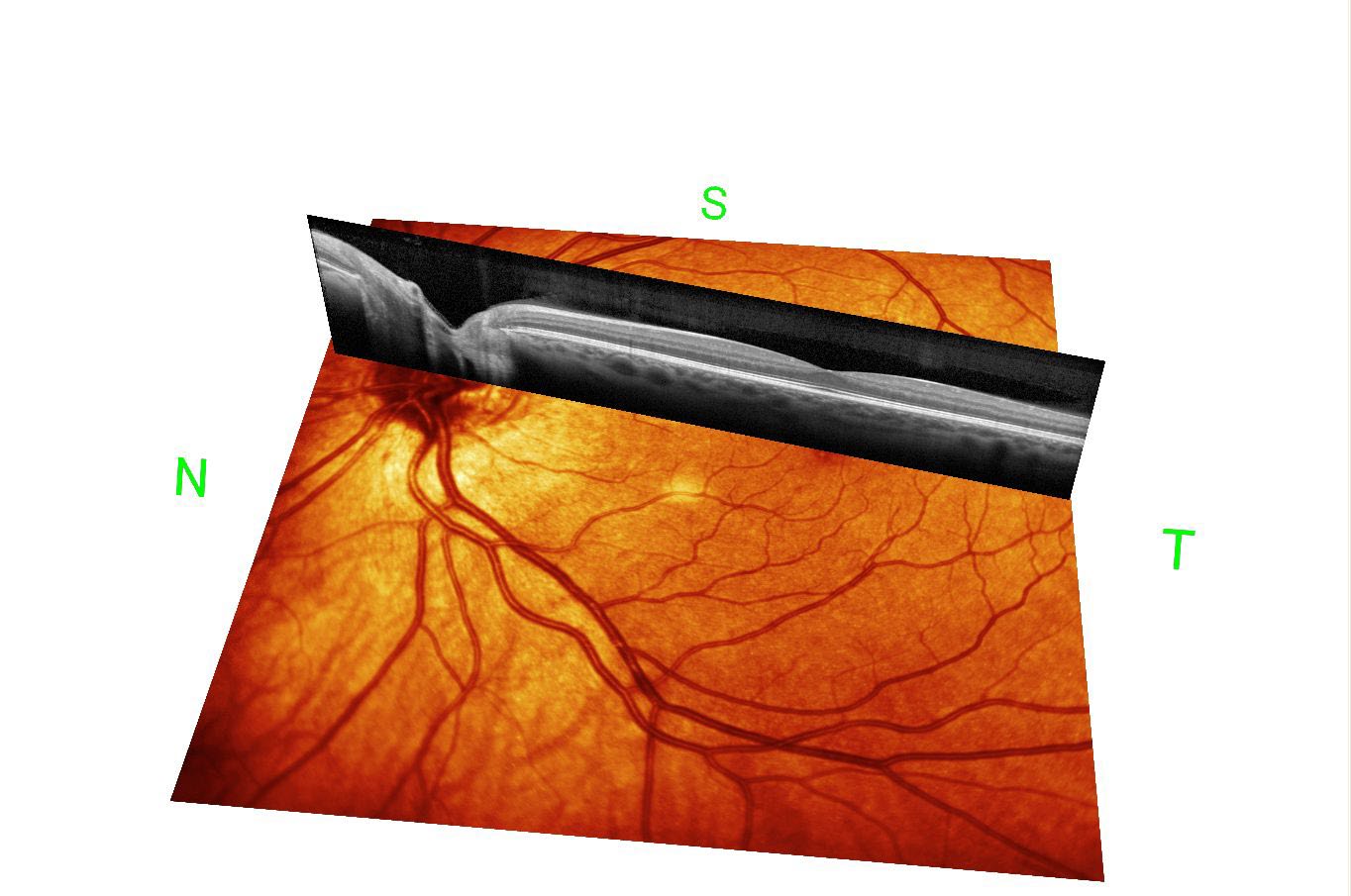
3. Optical Coherence Tomogram
The new optical coherence tomography combined with imaging system is very helpful for the diagnosis and monitoring of macular lesions.
How is macular degeneration treated?
1. Laser treatment
It is a traditional laser coagulation technique, which is not suitable for lesions in the central area of the macula
2. Photodynamic therapy
It is a mixture of photosensitizer VISUDYNE and cold laser activation, thereby destroying and blocking abnormal proliferating blood vessels under the retina. It can help patients preserve their existing vision or slow down vision loss.
Before patients receive photodynamic therapy, they will first undergo fundus fluorescein angiography, which will allow doctors to more clearly see the leakage and location of abnormally proliferating blood vessels. During photodynamic therapy, VISUDYNE is first injected intravenously, and then cold laser is irradiated a few minutes later to block and destroy the abnormal proliferating blood vessels in the macula.
3. Vitreous injection of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors
The drug is injected into the vitreous through the eyeball, reducing vascular leakage and bleeding by preventing abnormal blood vessel growth. It is generally recommended that patients receive three consecutive injections within three months. If new blood vessels are found to persist or reappear, the patient will need another course of treatment. Whether vision can be maintained or enhanced depends on the severity of the condition and the patient's response to treatment.
Will macular degeneration cause blindness?
If left untreated, it can eventually lead to blindness.